The most expressive part of the human face is the Smile, yet its brilliance is constantly challenged. We live in a world of high-definition close-ups, where a bright, confident Smile is often the first thing people notice. If you’ve ever wondered what truly separates a dazzling white tooth from a dull one, the answer lies in chemistry, not just scrubbing. Teeth Whitening is more than a cosmetic treatment; it’s a targeted science that unlocks your teeth‘s natural color, safely addressing years of discoloration. Understand the peroxide power and professional options available to you.
The Anatomy of Color and Stains: Why Teeth Lose Their Luster
To understand how Teeth Whitening works, we must first understand why teeth darken. A tooth is composed of several layers, but two are most relevant to color: the white, protective outer layer, enamel, and the softer, naturally yellow layer beneath it, called dentin.
Over time, the tooth enamel can wear thin, allowing the underlying dentin’s yellowish hue to show through. More importantly, the enamel itself is slightly porous and acts like a sponge, absorbing stains from foods and drinks. Consequently, this absorption leads to visible discolouration.
Stains are broadly categorized into two main types:
1. Extrinsic Stains
These Stains are on the exterior surface of the teeth. They are caused by the chromatic chemicals found in certain foods and drinks or deposited by smoking.
- Common Sources of Extrinsic Stains: Dark-colored drinks (like coffee, tea, and red wine), richly pigmented foods (berries, curries), and tobacco products.
- Solution: These surface stains are the easiest to treat. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and professional cleaning can often manage them, but whitening Gels provide the definitive solution.
2. Intrinsic Stains
These are deeper Stains that lie within the dentin or are embedded deep within the enamel. Intrinsic staining is much harder to treat because the discoloration is internal.
- Causes of Intrinsic Staining: Trauma to the tooth, certain medications taken during childhood (age-related), excessive Fluoride exposure, or past root canal treatments.
- Solution: This type of staining usually requires more aggressive, professional whitening sessions (non-vital bleaching for root canal treatments) or restorative work like crowns or veneers.
The Science of Tooth Whitening: Peroxide Power
The secret weapon in virtually every effective tooth whitening treatment is the peroxide molecule. Whether you purchase a kit at the counter or receive a powerful treatment at the dental office, the core active ingredients are variations of peroxide-based bleaching agents.
The Active Ingredients
There are two primary ingredients used in modern bleaching formulas:
- Hydrogen Peroxide: This is the faster, more aggressive agent. It is chemically simpler and begins the whitening reaction almost immediately upon contact with the tooth surface. It is often used for in-office treatment because of its speed and potency.
- Carbamide Peroxide: This is essentially a stabilized form of hydrogen peroxide. When it touches the mouth and interacts with water, it breaks down into hydrogen peroxide (about 1/3 of the total concentration) and urea. This slower, more gradual release makes carbamide peroxide ideal for at-home tray-based tooth bleaching systems or whitening strips. The prolonged duration allows for effective whitening over several weeks without excessive Sensitivity.
The Bleaching Reaction Explained
Whitening is not a superficial process; it’s a chemical reaction known as oxidation. The mechanism is as follows:
- Absorption: The peroxide-based Gels are placed in contact with the teeth.
- Penetration: The small peroxide molecules penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin.
- Oxidation: Inside the tooth, the peroxide molecules break the chemical bonds of the highly pigmented, large carbon molecules that cause the Stains.
- Color Change: These large, dark molecules are converted into smaller, less pigmented, or colorless molecules. Because they are smaller, they reflect light differently, making the tooth appear much brighter and whiter. This process permanently changes the intrinsic color of teeth.
This targeted chemical action ensures that while the tooth‘s color changes dramatically, the structural integrity of the tooth enamel remains unharmed. However, it is critical to use the appropriate concentration and follow the directions of a dental professional to avoid potential damage to the gums and teeth.
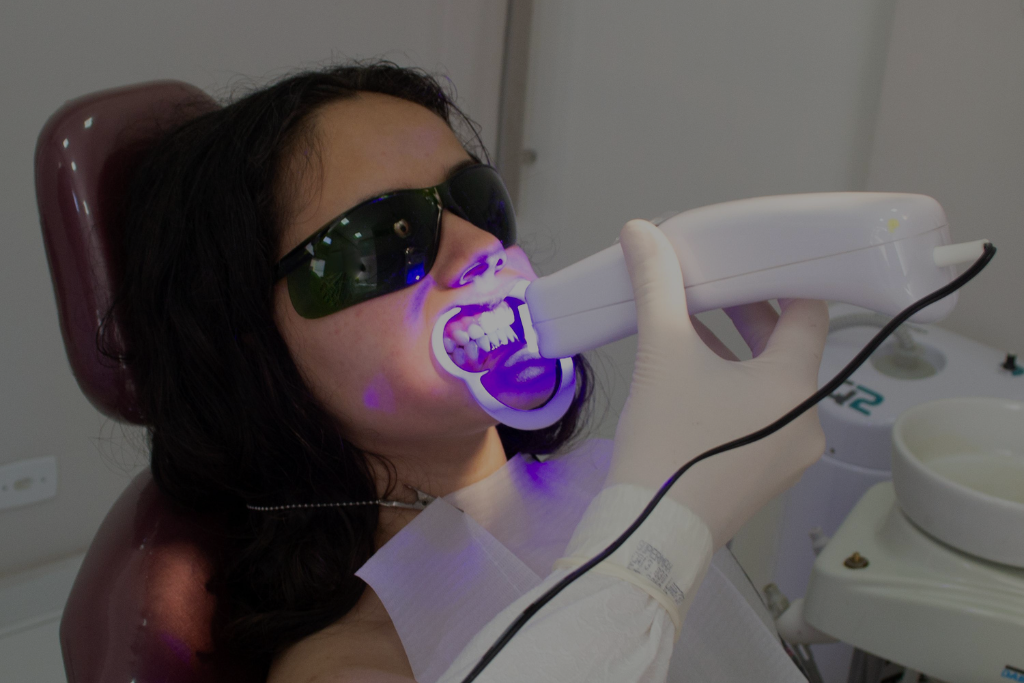
Professional Teeth Whitening Options
The most effective and safest route to a dramatically brighter Smile is through professional teeth whitening performed or supervised by a dentist. This allows for the use of high-concentration peroxide formulas in a controlled dental office setting.
1. In-Office Power Bleaching
This whitening method provides the fastest results, often brightening the Smile several shades in a single visit lasting 60 to 90 minutes.
- High Concentration: The dentist uses high-strength hydrogen peroxide Gels (up to 40% concentration).
- Gum Protection: The gums and soft tissues of the mouth are carefully protected with a liquid or rubber guard before the agent is applied to the tooth surface.
- Laser/LED Light Activation: While the peroxide does the chemical work, an accelerator, often a Laser or LED light, is sometimes used to slightly raise the temperature of the Gels, speeding up the reaction and improving the absorption of the peroxide-based bleaching agents. Multiple short sessions of application are typically performed.
2. Take-Home Tray-Based Tooth Bleaching Systems
This is the most common professional option and involves a lower, but still effective, concentration of carbamide peroxide Gels.
- Custom Guard: The dentist takes an impression of the teeth to create a custom-fitted mouthguard (guard). This custom tray ensures that the Gels are held tightly against the teeth for maximum contact and minimal spillage onto the gums.
- Duration: The patient wears the mouthguard for a specified duration (day or overnight) for several weeks, depending on the desired outcome and the initial discoloration.
At-Home and OTC Whitening Alternatives
For individuals with minor surface stains or those on a tight budget, there are several over-the-counter (OTC) products. These typically use lower, safer doses of peroxide-based formulas.
| Product Type | Active Ingredients | Pros | Cons |
| Whitening Strips (tooth whitening strips) | Low-concentration hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. | Convenient, easy to use, affordable. | Can cause uneven whitening or gum irritation if improperly applied; limited contact time. |
| Whitening Toothpaste | Mild abrasives or low levels of peroxide. | Excellent for preventing new staining and removing extrinsic stains. | Ineffective against intrinsic discoloration; not true bleaching. |
| Whitening Kit (Boil-and-Bite Tray) | Carbamide peroxide Gels and a generic mouthguard. | Better contact than strips; relatively affordable. | Generic guard fit often leads to gum irritation and wasted Gels. |
Export to Sheets
Non-Peroxide Approaches
The market is also flooded with non-peroxide methods, often promoted in magazines and online, such as activated charcoal and coconut oil.
- Charcoal and Abrasives: Toothpastes containing charcoal or other strong abrasives remove surface stains through mechanical scrubbing. While they can remove dark stains, they do not change the color of the tooth itself and, if used incorrectly, can cause long-term damage to the tooth enamel.
- Oil Pulling: Methods like oil pulling with coconut oil are primarily focused on general oral health benefits and possess no scientific evidence to support their claim as a true whitening method. They are not a bleaching treatment.
Managing Sensitivity and Maximizing Duration
One of the most common temporary effects of whitening is dental sensitivity (Sensitivity). This sharp, temporary pain occurs because the peroxide penetrates the enamel and causes minor, temporary dehydration of the tooth.
Tips for Managing Sensitivity
- Reduce Frequency: Reduce the duration of each whitening session or take a day or two off between treatments.
- Use Sensitivity-Friendly Ingredients: Brush with a toothpaste specially formulated for Sensitivity that contains ingredients like potassium nitrate, which calms the nerves in the tooth.
- Fluoride Treatments: Applying a high-concentration Fluoride Gels or using fluoride toothpaste immediately before and after treatment can help remineralize the enamel and reduce Sensitivity.
- Avoid: For the duration of the treatment, avoid extremely hot or cold foods and drinks.
Longevity and Maintenance
The color achieved after professional treatment can last anywhere from six months to three years, depending on your lifestyle. The key to maintaining a bright Smile is to minimize the staining sources (coffee, smoking, etc.) and use touch-up whitening Gels periodically. Regular dental office visits are crucial for assessment and proper maintenance.
Candidates for Teeth Whitening and When to Hold Back
While Teeth Whitening is safe for most individuals with natural teeth, it is not a universal solution.
Whitening Gels only work on natural teeth. Therefore, candidates for teeth whitening should be aware that existing restorative work will not change color:
- Crowns and Bridges: Existing crowns, veneers, or bridges will retain their original color. If you plan to replace these restorations, the whitening should be completed first to ensure the new work matches the brighter shade of your natural teeth.
- Fillings: Dental implants and existing fillings will also remain the original color.
- Root Canal Treatments: Intrinsic discoloration caused by a previous root canal treatment may not respond to traditional vital bleaching. Your dentist may recommend an internal non-vital bleaching method performed directly on the affected tooth.
A thorough examination, including assessing the type of staining, your health history, and previous dental work, is required before starting any treatment. Your dentist will use a Teeth Whitening Shade Guide to accurately chart your progress.

Why Choose Delta Park Dental?
At Delta Park Dental, we provide a full range of high-quality whitening options, from fast in-office Laser treatment to custom tray-based tooth bleaching systems. Our experienced team prioritizes patient safety, utilizing only professional-grade, peroxide-based bleaching agents and sensitivity-friendly ingredients. We are conveniently locationed, making professional treatment accessible and ensuring you receive personalized guidance throughout your journey to a brilliant Smile.
To help make essential dental care more affordable for our community, Delta Park Dental is a registered provider with the Canadian Dental Care Plan (CDCP).
The CDCP is a federal program designed to reduce financial barriers to oral health care for eligible Canadian residents who do not have access to private dental insurance.
Conclusion
The journey to a brighter Smile involves understanding the science behind the peroxide reaction and choosing the right treatment method. Whether you opt for the rapid, controlled power of an in-office Laser process or the gradual duration of an at-home kit, the key is consulting your dentist. By understanding the science of Teeth Whitening, you invest in a brighter, healthier Smile that lasts, boosting your confidence and overall health.
Ready to unleash the science of your Smile? Contact Delta Park Dental today to schedule your consultation.
Tags
- Dental Bridges
- Veeners Dental
- Veeners Dental Near Me
- Root Canal Treatment near me
- Dental Bonding In Brampton
- Bridge Dental Brampton
- Dental Bridge Brampton
- Emergency Dental Brampton
- Dental Bridges Near Me
- Dental Veneers Near Me
- Veneers Dental
- Root Canal Therapy
- Dental Emergency Near Me
- Emergency Dentistry
- Brampton Dental Implant
- Dental Implant Brampton
- Dental Implant
- Dental Implant in Brampton
- Dental Veneers
- Dental Veneer
- Dental Filling Before and After
- Whiten Teeth
- crown dental implant
- Dental Crown in Brampton
- Whitening Teeth
- Wisdom Teeth Removal
- Dental Bonding
- Dental Bonding Near me
- Dental Crown Near Me
- Dental Crown Brampton
- Wisdom Teeth Extraction
- Wisdom Tooth Removal
- Dental Crown
- Dental Teeth Whitening
- Wisdom Tooth Extraction
- Dental Filling Brampton
- Dental Filling
- Teeth Whitening Dentist
- Dental Fillings
- Teeth Extraction
- Dental Filling Near me
- Teeth Whitening Near Me
- Dental Emergency Brampton
- Tooth Extraction
- Emergency Dentistry Services



